Used in LED panels Flip-chip Technology is a method of LED manufacturing in which the electrodes of the LED chip are bonded directly to the substrate in an inverted form, as opposed to the traditional "wire bonding" method. This method aims to improve performance and efficiency, and is particularly popular in high-resolution LED displays.
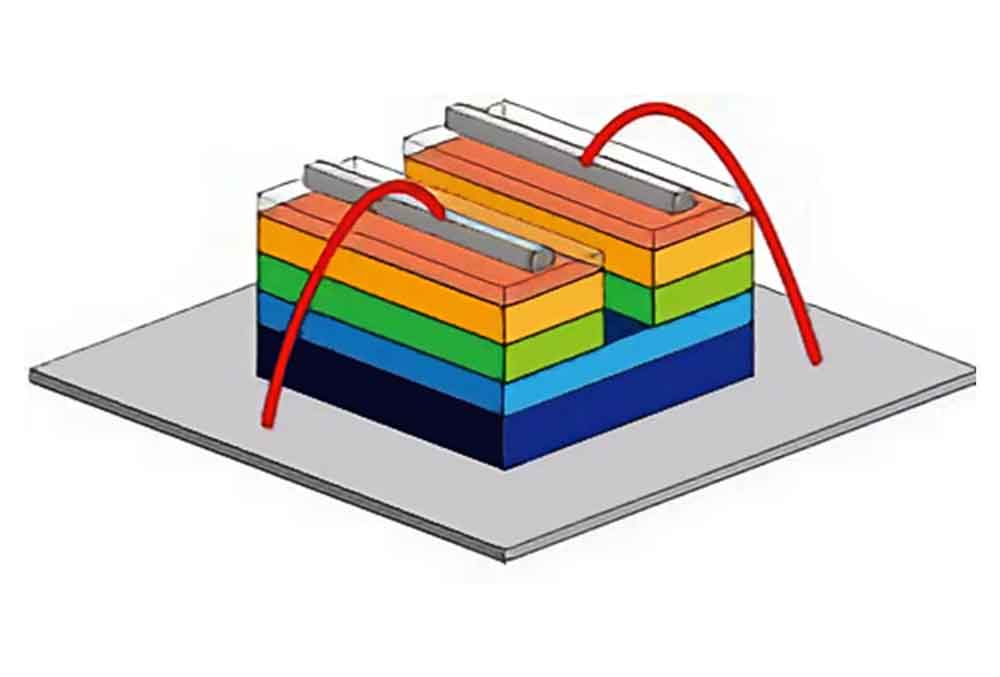
Wire Bonding
In traditional wire bonding, the electrodes are connected to the substrate by wires with the electrodes facing up.
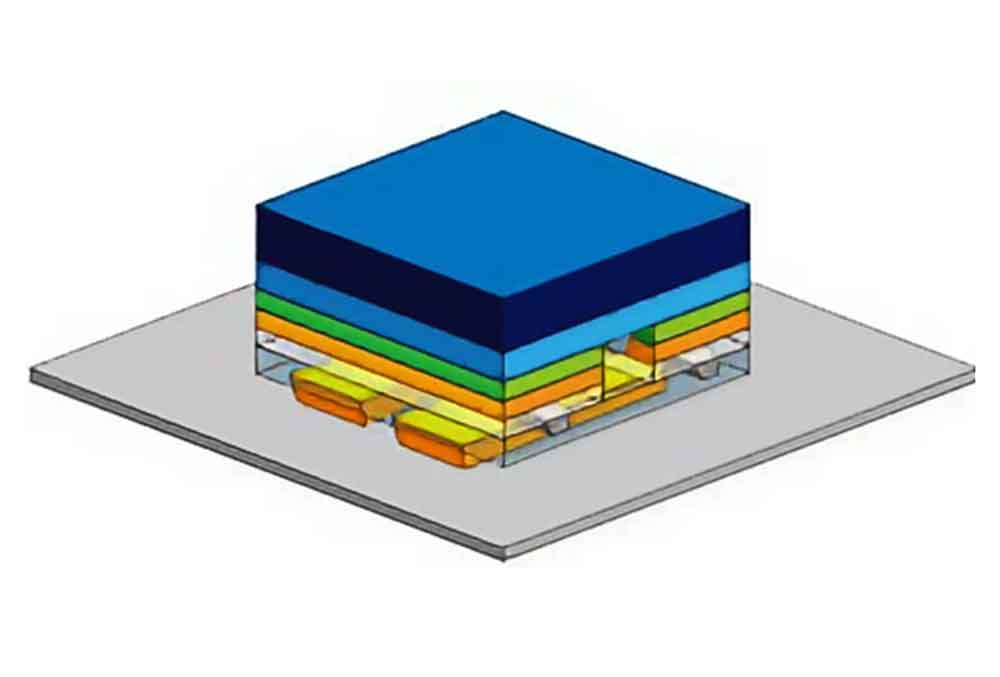
Flip-chip
Splicing the electrodes down, with the light-emitting side of the LED chip facing away from the board. The chip is connected directly to the substrate.
Improve light efficiency
Compared to wire bonding, the electrodes take up less space, resulting in a larger light-emitting area and higher light efficiency. You also don't have to worry about wires blocking light, so you can realize brighter LEDs.
Cable Free
In traditional wire bonding, the electrodes are connected to the board by a wire pointing upward, but Flip-chip eliminates this wire, making it structurally simpler.
Durability
The absence of wires increases resistance to physical damage and makes the LED panel more durable.
Efficient heat dissipation
The flip-chip approach puts the LED chip in direct contact with the substrate, resulting in a shorter heat dissipation path. This makes it easier to manage heat, and allows for stable performance even with high-power LEDs.
Smaller pixel pitch
Because Flip-chip has no wires, LED chips can be placed closer together, resulting in a smaller pixel pitch suitable for high-resolution displays. This is especially important for small displays and micro-LED panels.
In conclusion, Flip-chip is a technology that can maximize the performance of LED displays, providing higher light efficiency, thermal management, durability, and more, making it ideal for high-resolution and miniaturized displays.